How to Send Emails in Node.js: SMTP, Email APIs, and Notification Services (With Code Tutorials)
Adeyinka Adegbenro
February 23, 2021

Nearly every modern web app needs to send transactional emails in response to user activity — things like account creation, password resets, order confirmations, or verification codes. These emails are essential for keeping users informed and ensuring smooth user experiences.
If you're building with Node.js, there are several ways to implement email delivery. This guide explores three common approaches:
- SMTP – Set up and manage your own mail server using libraries like Nodemailer
- Email API – Use hosted providers like SendGrid or Mailgun for faster setup and improved deliverability
- Notification Service – Use a multichannel service like Courier to centralize message design, logic, and delivery (see our SendGrid + Node.js tutorial)
We’ll walk through the pros and cons of each, and include step-by-step code examples so you can choose the best method for your app.
3 Ways to Send Email with Node.js
Node.js gives you several options for sending email from your application. In this guide, we’ll compare the three most common approaches:
- SMTP – Send emails directly by managing your own mail server
- Email API – Use a hosted service like SendGrid or Mailgun for easier integration and better deliverability
- Notification Service – Use a platform like Courier to manage multichannel notifications with a single API
We’ll break down how each method works, walk through pros and cons, and include hands-on code examples so you can choose the right solution for your stack.
1. Using SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a standard protocol for sending emails across networks. It serves as a relay service that delivers messages from one mail server to another.
When you send an email using a client like Gmail, an SMTP server handles the outgoing message. It communicates with the recipient’s server using SMTP commands, negotiating delivery based on the message headers, destination, and authentication. Most email clients come pre-configured with their own SMTP servers.
✅ Advantages of using SMTP
- Widely supported: SMTP is a universally adopted standard. It's straightforward to set up with libraries like Nodemailer, and integrates easily into most web applications.
- Complete control: Running your own SMTP server gives you full control over how messages are composed, authenticated, and sent — without relying on third-party services.
❌ Drawbacks of using SMTP
- Security concerns: SMTP is inherently insecure without proper authentication and encryption. It’s vulnerable to spam, spoofing, and data breaches unless hardened with TLS, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- Complex maintenance: Hosting your own mail server means managing infrastructure long-term — from uptime to spam filtering to deliverability optimization. Most teams prefer to avoid this overhead.
- Slower performance and limited feedback: SMTP involves multiple handshakes between servers, making it slower than API-based alternatives. If a message fails, debugging can be difficult without proper logging or feedback from the receiving server.
- Reliability issues: Your server’s IP may be blacklisted, or firewalls might block required ports, leading to delivery failures without clear diagnostics.
🛠️ If you choose to go the SMTP route, use a sandbox service like Mailtrap for safe testing, and make sure your production server is configured with secure defaults.
2. Using an Email API
Email APIs let you send messages from your application through a hosted provider, without needing to run your own mail server. They handle message assembly, delivery, and reputation management on your behalf.
These APIs are ideal when you need a scalable, reliable, and developer-friendly way to send transactional emails — like password resets, receipts, or notifications — with minimal setup.
Popular email API services include:
Most providers offer free or low-cost plans with generous usage limits to get started.
✅ Advantages of using an Email API
- Fast setup: With clear documentation and SDKs in popular languages, you can get started in minutes.
- Highly scalable: Built to support high-volume workloads with built-in queuing and retry mechanisms.
- Better deliverability: Providers maintain sending IPs and reputations to help ensure your messages land in the inbox.
- More secure: Uses API keys instead of username/password authentication, and enforces TLS encryption.
❌ Drawbacks of using an Email API
- Third-party dependency: You’re outsourcing message delivery to a provider. If their service goes down or they change pricing, you may need to migrate.
- Limited channel coverage: If your app needs to notify users through additional channels — like SMS, push, chat apps (e.g., Slack, Microsoft Teams, Discord), or in-app inboxes — you’ll have to integrate and manage each of those channels separately.
- Vendor lock-in risk: Switching providers often means rewriting templates or updating your integration logic, especially if you're deeply tied to one API's format or features.
🔍 Before choosing a provider, compare key features, delivery performance, uptime SLAs, and support for your use case.
3. Using a Notification Service
A notification service like Courier gives you higher-level building blocks to manage notification logic — and lets you reach users across every channel from one place.
You can bring your own provider for each channel. For email, that could be your own SMTP server or a hosted email API like SendGrid, Postmark, or Amazon SES. A notification service can also support failover to alternate providers if one becomes unavailable.
With a notification service, you can add new channels or switch providers without rewriting your app’s business logic. If you need to notify users across email, SMS, push, or chat apps like Slack and WhatsApp — you can do it all from a single platform.
Courier offers a layer of abstraction on top of email APIs — giving you tools for design, orchestration, and observability. You can visually design emails, create delivery rules and workflows, and monitor delivery events in real time — without having to redeploy code.
Advantages of using a multichannel notification service
Some of the key benefits of using a service like Courier:
- Send options: Send notifications via API, event-based automation, or one-time messages from a web UI
- Multichannel routing: Automate delivery across channels like email, push, SMS, chat apps (e.g., Slack, Teams), or in-app inboxes
- Unified logging and analytics: View all delivery logs across channels and providers in one place
- User preferences: Built-in logic and hosted UI for users to manage notification topics, channels, and frequency
- Send limits and throttling: Prevent spam or over-notification
- Batching and digesting: Bundle related content into a single digest based on rules or user preferences
- Out-of-box integrations: Easily connect to email and SMS providers, CDPs, auth tools, i18n libraries, observability platforms, and more
These features dramatically reduce the engineering effort required to support different notification use cases — and eliminate the need to maintain separate code for each channel or provider.
Another advantage: non-technical teammates can edit content, styling, or branding directly in Courier without needing to touch code. You can preview notifications using test data and safely troubleshoot issues in a dedicated test environment before going live.
Drawbacks of using a multichannel notification service
Because you're still sending messages through email APIs or SMTP, you remain dependent on a third-party service for delivery. However, notification services mitigate this risk with:
- Provider failover: e.g., fallback to Postmark if SendGrid is down
- Channel failover: e.g., retry with SMS or push if email isn’t delivered or read
This extra resilience — combined with flexibility and visibility — makes notification services an attractive option for most teams. Courier’s free plan includes 10,000 notifications per month, making it easy to try out.
Tutorial: How to send emails with Nodemailer and SMTP
Nodemailer is a Node.js module used for sending emails and is the most popular Node.js email package. You can use Nodemailer to create HTML or plain-text emails, add attachments, and send your emails through different transport methods, including built-in SMTP support. It requires Node.js 6.0 or newer.
Let’s walk through how to send email using Nodemailer. The first step is to create a Node.js application:
Copied!
mkdir email-nodeapp && cd email-nodeappnpm init -y
Here you’ve created a folder and initialized a package.json file using the npm init command. The -y flag is there to skip the interactive back-and-forth questions by npm.
Next, install the Nodemailer module:
Copied!
npm install nodemailer
Nodemailer’s createTransport function specifies which method you want to use for sending email. It takes the connection data and credentials as an argument. In this case, since SMTP is the preferred transport, you will need to define an SMTP host, port, and credential password for accessing a host SMTP server.
To get a host URL, you need an SMTP server. For development purposes, you can use Mailtrap, or a similar service, to serve as a fake SMTP server. A fake SMTP server lets you avoid cluttering your real account with multiple tests while still seeing how your test emails behave — do all the buttons work the way they’re supposed to, is the formatting still correct after sending, and so on.
Create a Mailtrap account if you don’t already have one. In the Integrations dropdown on the dashboard, select Nodemailer and copy the credentials displayed.
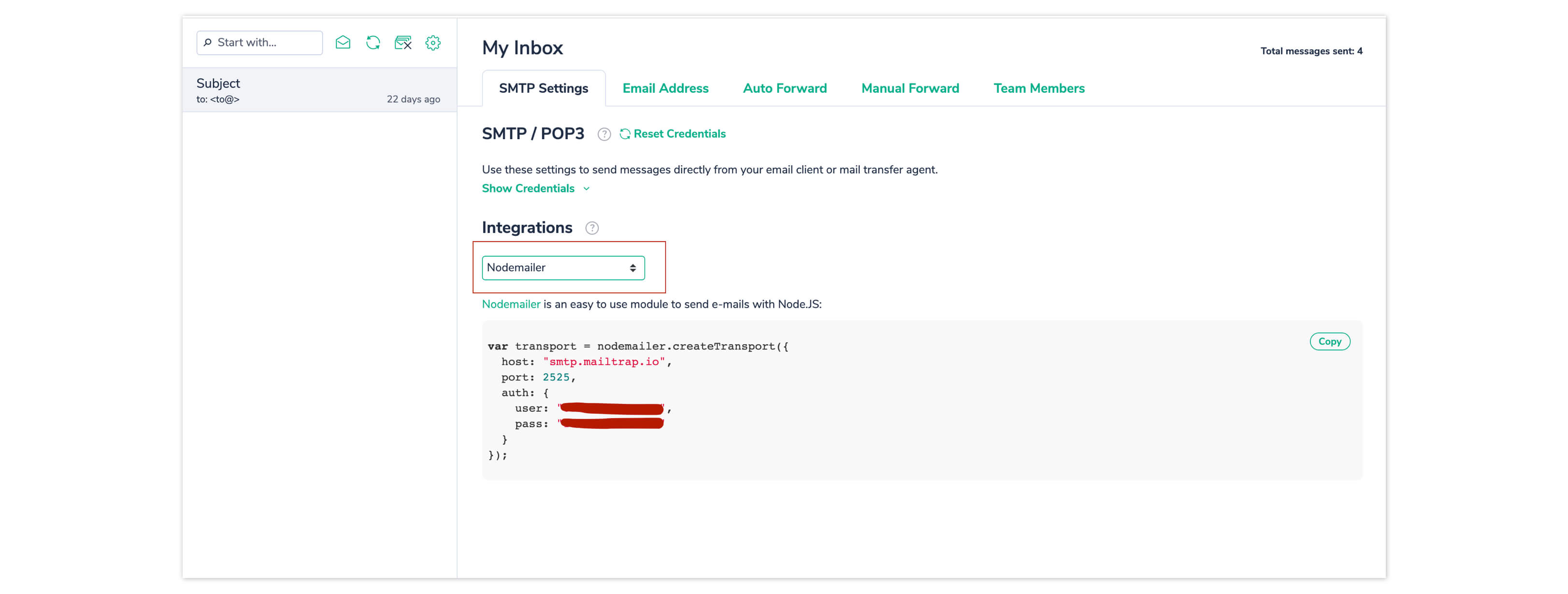
Create an email.js file and add the following:
Copied!
const nodemailer = require('nodemailer');let transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({host: 'smtp.mailtrap.io',port: 2525,auth: {user: "<user>",pass: "<pass>"}})
Substitute the host, user, and password with the Mailtrap credentials you copied from the dashboard above. Now you can send an email using the sendMail method of Nodemailer’s createTransport function.
Append the following to the email.js:
Copied!
message = {from: "from-example@email.com",to: "to-example@email.com",subject: "Subject",text: "Hello SMTP Email"}transporter.sendMail(message, **function**(err, info) {if (err) {console.log(err)} else {console.log(info);}
Nodemailer also supports sending emails using HTML. All you need to do is add the html attribute to your message object like so:
Copied!
message = {from: "from@email.com",to: "to@email.com",subject: "Subject",html: "<h1>Hello SMTP Email</h1>"}
To test that it works, go to your terminal and run:
Copied!
node email.js
Go to your Mailtrap dashboard to see your email was received.
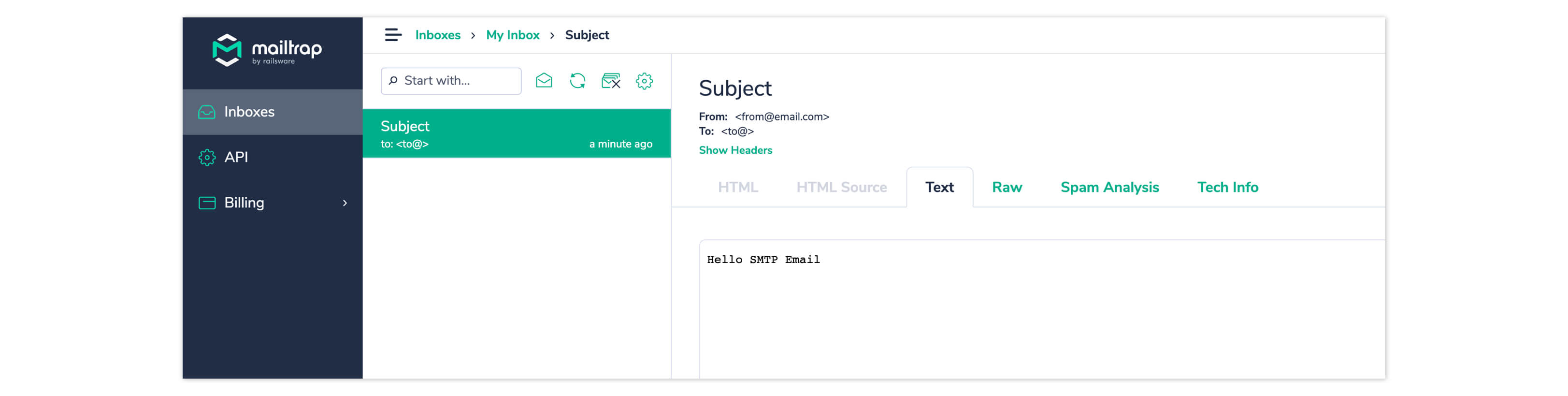
Tutorial: How to send emails using a transactional email API
There are a variety of email-as-a-service platforms and APIs, such as SendGrid and Mailgun, among others. For this article, I’ll demonstrate sending emails from within a Node application using SendGrid, which allows you to send up to 100 emails per month for free.
To start sending emails with SendGrid, the first step is to sign up for the service. Then you’ll need to create a SendGrid API key for sending email.
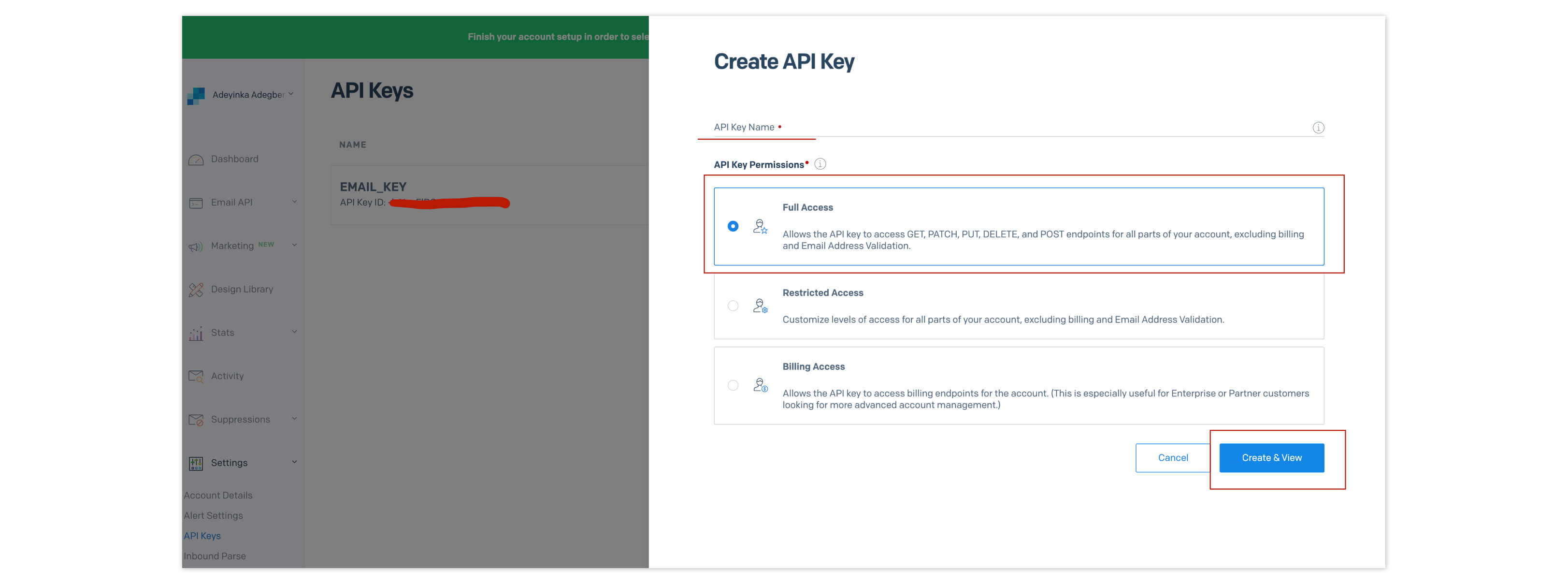
To create an API key, go to Settings > API Keys on SendGrid’s dashboard, then click “Create API Key.” Give the key a name, select “Full Access,” then click “Create & View.” Copy your API key and keep it safe for later use.
Next, install the SendGrid JavaScript client with npm:
Copied!
npm install --save @sendgrid/mail
Create a file in your project directory named sendgrid.js:
Copied!
touch sendgrid.js
In the sendgrid.js file, add the following lines of code:
Copied!
const sendgrid = require('@sendgrid/mail');const SENDGRID_API_KEY = "<SENDGRID_API_KEY>"sendgrid.setApiKey(SENDGRID_API_KEY)const msg = {to: 'test@example.com',// Change to your recipientfrom: 'test@example.com',// Change to your verified sendersubject: 'Sending with SendGrid Is Fun',text: 'and easy to do anywhere, even with Node.js',html: '<strong>and easy to do anywhere, even with Node.js</strong>',}sendgrid.send(msg).then((resp) => {console.log('Email sent\n', resp)}).catch((error) => {console.error(error)})
Replace the variable SENDGRID_API_KEY with the SendGrid API key you created previously and make sure the email address in the From field has been verified by SendGrid. You can do this by creating a sender identity. This verifies that the email address actually belongs to you. Also, replace the email address in the To field from test@example.com to your test recipient.
To test that it works, run:
Copied!
node sendgrid.js
To see if your email was delivered, check the SendGrid dashboard, and on the sidebar, select “Activity.” There, you should see the email you just sent. SendGrid will show you whether it was delivered or not and whether it has been opened.
Tutorial: How to send emails using a multichannel notification service
Courier is a multichannel notifications platform that enables you to reach your users on any channel using one uniform API. With Courier, you can bring your own email service provider, including SMTP or Gmail, or any of the popular email APIs like SendGrid, Amazon SES, and Postmark.
To start using Courier, create an account. You can send up to 10,000 notifications per month for free. During the onboarding flow, you’ll be asked to give Courier permission to send email on your behalf from your Gmail account. You can skip this step if you’re planning on using a different ESP, but we recommend setting it up as the fastest way to test out sending from Courier.
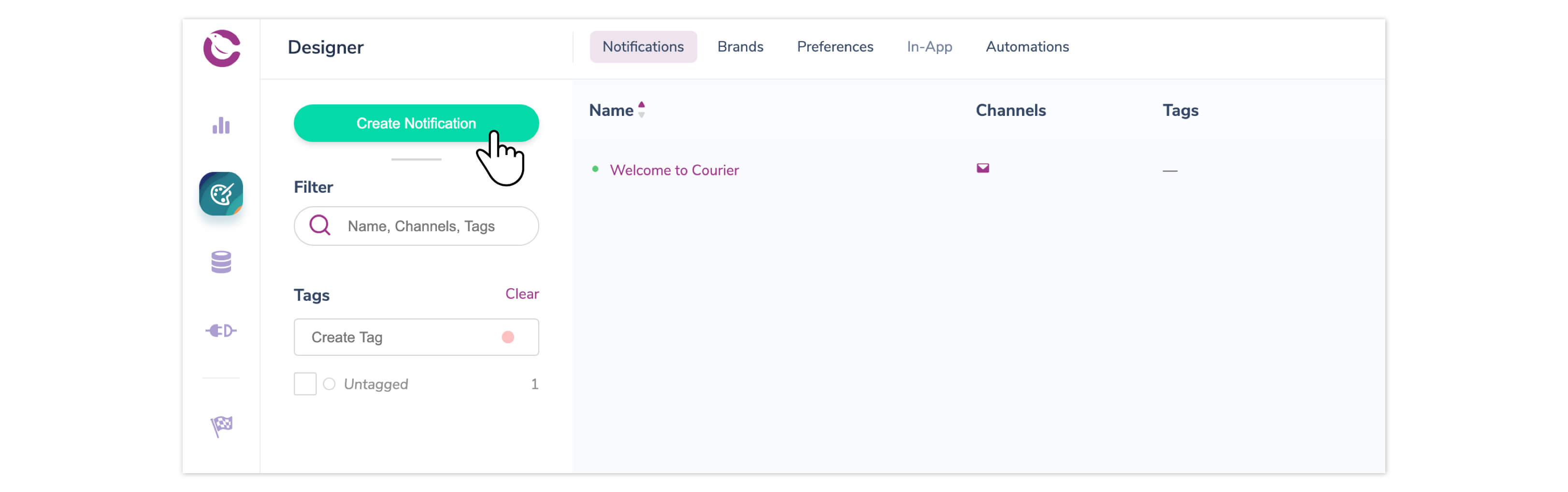
To use Courier to send transactional emails, head to the Courier dashboard and select Designer on the lefthand menu. Then, click the “Create Notification” button.
Select Gmail in the provider selection modal and hit “Continue”.
From there, you’ll want to add the content for your email notification. You can use the toolbar to drag and drop blocks for text, images, buttons, and more. You can even add Markdown or add code blocks to further customize your email.
Next, send the email notification from within Node.js using the Courier npm package@trycourier/courier. To install it, run:
Copied!
npm install @trycourier/courier
Create a file in your app directory named courier.js:
Copied!
touch courier.js
Courier will automatically generate a code snippet for your notification, which you can copy-paste from the Send tab. Add the following lines of code to the file:
Copied!
const { CourierClient } = require("@trycourier/courier");const courier = CourierClient({ authorizationToken: "<AUTH_TOKEN>" });courier.send({eventId: "<EVENT ID>", *// your Notification IDrecipientId: "<RECIPIENT_ID", *// usually your system's User IDprofile: {email: "<EMAIL_ADDRESS>"},data: {} *// optional variables for merging into templates }).then((resp) => {console.log('Email sent', resp)}).catch((error) => {console.error(error)});
The Courier package is imported into the file, and the Courier client is instantiated. The client takes an authentication token, which you can get from the Courier notification settings created earlier. Click the gear icon from within your notification and copy the masked auth token.
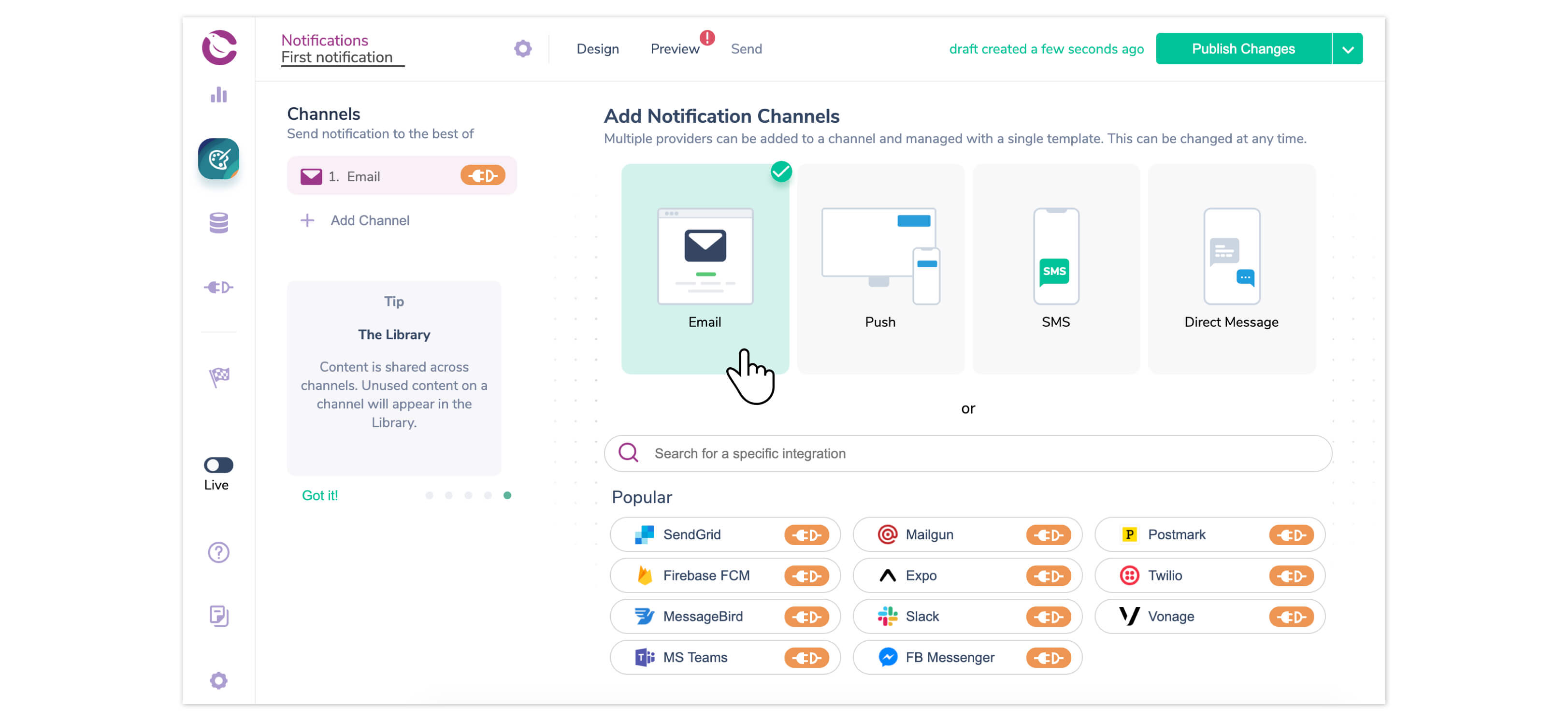
The Courier client has a send method which takes an event ID, which is either the notification ID or custom event that you’ve mapped to your notification. The recipient Id should be a unique string you can use to identify the recipient and look them up in data logs. Note that email refers to the email address of the recipient.
To check the status of your email, head to the Data tab in your Courier dashboard. Courier will tell you if your email has been delivered, opened, and/or clicked. Courier will also tell you if there are any errors and when in the delivery pipeline they occurred.
Conclusion
Email is still foundational for transactional communication — but it’s no longer the only channel users rely on. From SMS and push notifications to Slack and in-app inboxes, modern applications need to reach users where they are.
If you're using Node.js, you have a few ways to implement email delivery:
- SMTP gives you full control but comes with high setup and maintenance costs
- Email APIs like SendGrid and Mailgun offer quick integration but are limited to a single channel
- Notification platforms like Courier give you a unified, future-proof way to manage messaging across every channel
The world is shifting toward multichannel communication. Users expect personalized, timely updates across email, mobile, and chat — and managing this complexity manually is no longer sustainable. That’s why we recommend Courier: a modern platform built for the realities of today’s apps. It lets you bring your own email provider (SMTP or API), design notifications visually or with code, and seamlessly expand to new channels — all from a single API.
🚀 Get started free — Sign up for Courier and start building multichannel notifications in minutes.
Similar resources
The Notification Platform Developers Choose
Most notification platforms built dashboards first and added developer tools later. Courier did the opposite. With a CLI that handles real workflows, MCP integration with setup management, typed SDKs in seven languages, and SOC 2 Type 2 certification, Courier is built for teams that ship. This isn't marketing copy: Twilio chose Courier to unify notifications across their 10M+ developer platform. LaunchDarkly uses Courier to power feature release workflows. When the companies that build developer infrastructure choose your notification platform, that says something about the technical foundation.
By Kyle Seyler
January 26, 2026
Vibe Coding Notifications: How to Use Courier with Cursor or Claude Code
Courier's MCP server lets AI coding tools like Cursor and Claude Code interact directly with your notification infrastructure. Unlike Knock and Novu's MCP servers that focus on API operations, Courier's includes embedded installation guides for Node, Python, Flutter, React, and other platforms. When you prompt "add Courier to my app," your AI assistant pulls accurate setup instructions rather than relying on outdated training data. OneSignal's MCP is community-maintained, not official. Courier supports 50+ providers, native Slack/Teams integration, drop-in inbox and preference components, and a free tier of 10,000 notifications/month. Configure in Cursor with "url": "https://mcp.courier.com" and "headers": { "api_key": "YOUR_KEY" }.
By Kyle Seyler
January 22, 2026

How Top Notification Platforms Handle Quiet Hours & Delivery Windows in 2026
No platform offers per-template delivery windows in 2026—it's either per-workflow (Customer.io, Knock), per-campaign (Braze), or global settings. This comparison shows exactly how six platforms handle quiet hours and send time controls based on their documentation and API specs. Braze leads on AI timing (23% open rate lift from Intelligent Timing across their customer base). Novu is the only platform letting subscribers set their own delivery windows. Customer.io and Knock require manual workflow configuration. OneSignal's strength is push-specific optimization across 300K+ apps. Courier combines per-node flexibility with API control. Includes feature matrix, timezone handling, and frequency capping differences.
By Kyle Seyler
January 16, 2026
© 2026 Courier. All rights reserved.