Push Notification Fallbacks: Ensuring Message Delivery with Email, Slack, SMS
Kyle Seyler
September 16, 2025

Table of contents
How Courier Handles Push Notification Fallbacks
What Are Channel Fallbacks?
When Do You Need Push Notification Fallbacks?
How Do You Configure Channel Routing in Courier?
What Are the Best Practices for Fallback Configuration?
How Do You Handle Provider Failures?
What About Cost Optimization?
How Do You Monitor Fallback Performance?
Advanced Fallback Patterns
Common Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
What Are Real-World Fallback Use Cases?
Setting Up Your First Fallback Configuration with Courier
What's Next?
Frequently Asked Questions
Push Notification Fallbacks: Ensuring Message Delivery with Email, SMS, & Slack
TL;DR: Push notifications have the highest engagement rates, but what happens when they fail? Learn how to implement intelligent fallback strategies using email, SMS, Slack, and Microsoft Teams to ensure your critical messages always reach users. We'll cover channel routing, timeout configuration, and best practices for building a resilient notification system.
How Courier Handles Push Notification Fallbacks
Push notifications deliver instant engagement, but they're not always available. Users might have disabled notifications, uninstalled your app, or be using devices without push support. That's where intelligent fallback strategies become essential.
Courier's multi-channel routing automatically handles these scenarios, seamlessly switching to email, in-app, SMS, Slack, or Microsoft Teams when push delivery fails. This ensures your messages reach users through their next best available channel.
What Are Channel Fallbacks?
Channel fallbacks create a delivery hierarchy for your notifications. When your primary channel (push) is unavailable or fails, Courier automatically tries the next channel in your defined sequence. This happens without any manual intervention, keeping your notification delivery reliable and consistent.
Here's how the fallback flow works:
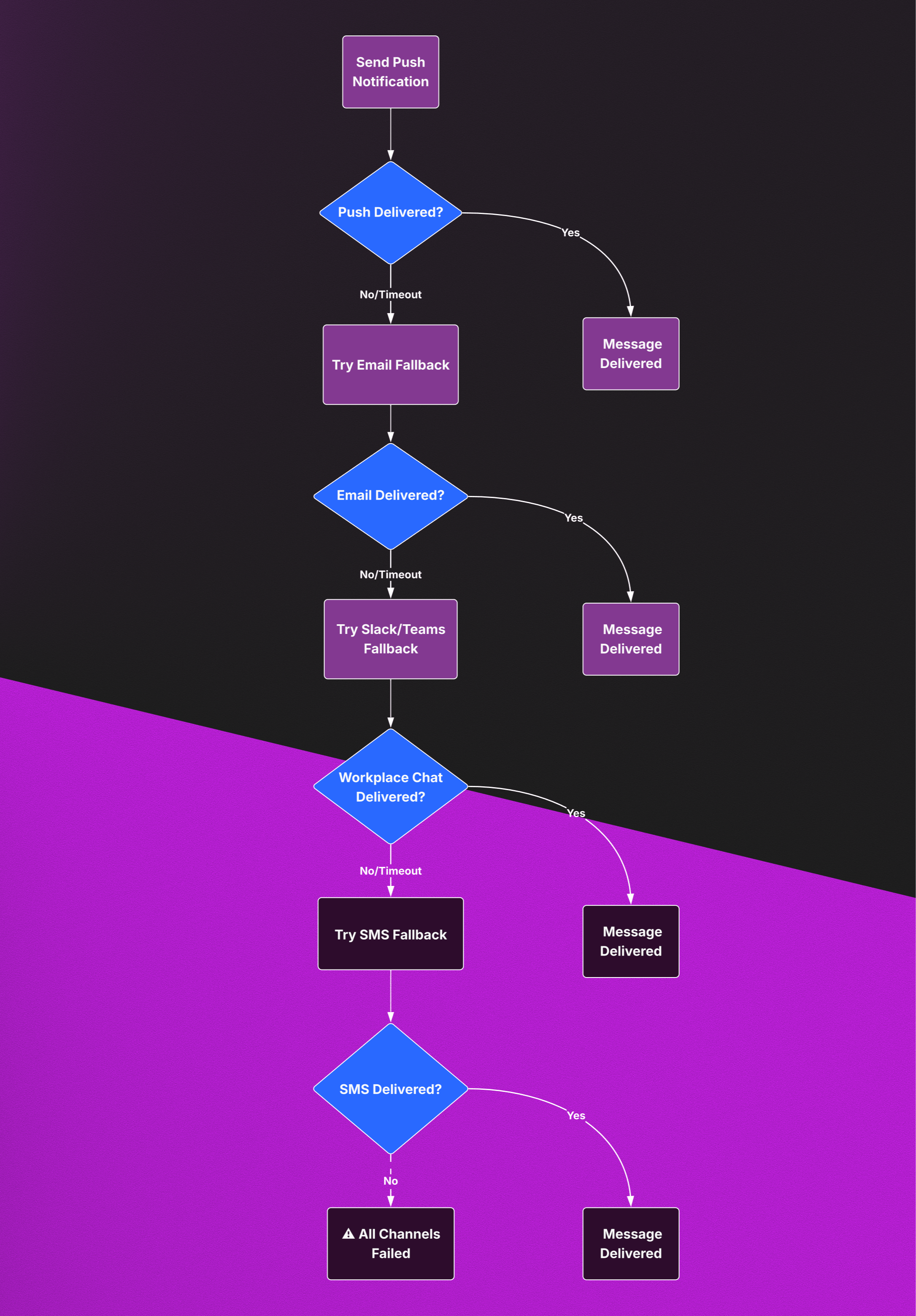
This automated sequence ensures your critical messages reach users through their next best available channel:
- Attempt push notification first (highest engagement)
- Fallback to email if push fails (detailed content)
- Try workplace chat like Slack or Microsoft Teams (immediate workplace visibility)
- Final attempt via SMS for critical messages (highest deliverability)
When Do You Need Push Notification Fallbacks?
Common Scenarios Where Push Fails
Push notifications aren't guaranteed to reach every user. Understanding when and why push delivery fails helps you design better fallback strategies:
- Users opting out or disabling notification permissions: Many users turn off notifications entirely
- Devices being offline or in restricted states: iOS Focus Mode, Do Not Disturb, or airplane mode
- Uninstalled apps or expired push tokens: Tokens become invalid when apps are removed
- Device limitations: Older devices or custom ROMs may have push issues
- Provider outages: FCM or APNs experiencing downtime affects millions
- Network connectivity problems: Poor cellular or WiFi can prevent delivery
Types of Messages That Need Fallbacks
Not every notification requires multiple fallback channels. Prioritize fallbacks for:
Critical Communications:
- Security alerts: Password changes, suspicious login attempts, two-factor authentication
- Transaction confirmations: Payment receipts, order updates, billing failures
- Time-sensitive updates: Appointment reminders, delivery notifications, event alerts
- Account actions: Verification codes, account recovery, subscription changes
- System alerts: Service disruptions, urgent maintenance, data breaches
High-Value Opportunities:
- New Business Updates: Alerts that some new opportunity has opened up
- Abandoned cart recovery: Re-engaging users who left items in their cart
- Onboarding sequences: Critical steps that impact user activation
- Renewal reminders: Subscription or service renewals with revenue impact
How Do You Configure Channel Routing in Courier?
Setting up intelligent fallback messaging doesn't require complex infrastructure or custom retry logic. Courier handles the heavy lifting while giving you complete control over how and when messages fall back between channels.
The beauty of Courier's approach is its flexibility. You can configure fallbacks through visual designers for quick setup, or use programmatic APIs for dynamic, user-specific routing decisions. Most teams start with simple configurations and evolve their strategies based on real delivery data.
Smart Routing with the Send API
When you need dynamic control over fallback behavior, Courier's Send API lets you define routing rules that adapt to each message's importance and user context. The system automatically handles the complexity of checking delivery status, managing timeouts, and switching between channels seamlessly.
For example, a payment confirmation might try push notification first for immediate awareness, then fall back to email for detailed receipt information, and finally attempt SMS if the user needs urgent notification about a failed transaction. Courier manages this entire sequence automatically based on your configuration.
Copied!
const courier = new CourierClient({authorizationToken: process.env.COURIER_AUTH_TOKEN});await courier.send({message: {to: { user_id: "team_lead" },content: {title: "System Alert",body: "Database connection issues detected. Please investigate."},routing: {method: "single",channels: ["push", "slack", "sms", "email"]},timeout: {channel: 300000 // 5 minutes per channel}}});
Visual Template Configuration
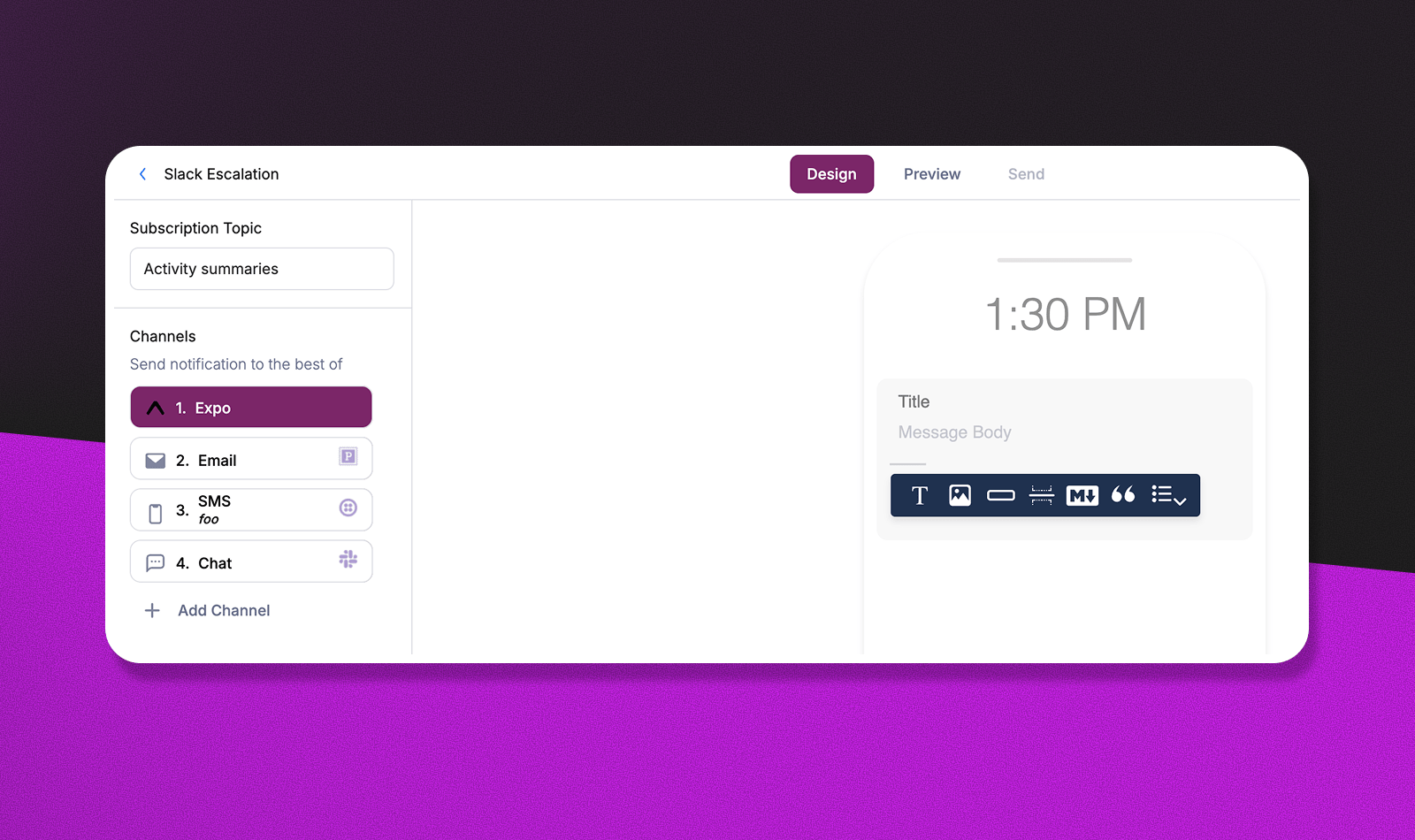
Many teams prefer the visual approach, especially for standardized notification types. Courier's template designer lets you drag and drop channels into priority order, set timeout periods, and define fallback conditions without writing any code. This approach works particularly well for operational teams who need to adjust routing strategies quickly based on changing business needs or channel performance.
What Are the Best Practices for Fallback Configuration?
Channel Selection by Message Type
Different message types require different fallback strategies. Here's how to match channels to content:
| Message Type | Primary | First Fallback | Second Fallback | Final Fallback | Grace Period | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Security Alerts | Push | SMS | Slack/Teams | 2-5 minutes | Immediate attention required | |
| Order Updates | Push | Slack/Teams | SMS | 30 minutes | Detailed tracking info needed | |
| Payment Failures | Push | SMS | Slack/Teams | 5 minutes | Urgent action required | |
| Event Reminders | Push | Slack/Teams | SMS | 24 hours | Allow time for planning | |
| New Business | Push | Slack/Teams | SMS | 2-5 minutes | Time-sensitive opportunity | |
| Billing Notices | Push | Slack/Teams | SMS | 24 hours | Detailed information preferred | |
| System Downtime | Push | Slack/Teams | SMS | Immediate | Critical service impact | |
| Verification Codes | SMS | Push | Slack/Teams | N/A | Highest deliverability needed |
Timing Your Fallback Strategy
The grace period between channels is crucial for user experience:
- Use workplace chat or email as your first fallback
- they're less disruptive than SMS
- Consider workplace context
- Slack and Teams are perfect for business-critical alerts during work hours
- Add a short grace period (2-5 minutes) before sending fallback messages to give users time to engage
- Don't overwhelm users
- limit how often fallback messages are sent across channels
- Always respect user preferences
- only message users who've opted in to that channel
Timing Your Fallback Strategy
Getting the timing right is crucial for user experience and delivery success. Too aggressive, and you overwhelm users with duplicate messages. Too conservative, and critical information arrives too late to be useful.
Here's how different fallback strategies compare:
| Strategy | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggressive (2-5 min) | ✅ Fast delivery ✅ High reliability ✅ Good for urgent alerts | ❌ May duplicate messages ❌ Higher costs ❌ Can annoy users | Security alerts, payment failures |
| Balanced (30 min - 2 hours) | ✅ Good user experience ✅ Cost effective ✅ Respects user behavior | ❌ Slower for urgent messages ❌ May miss time-sensitive windows | Order updates, appointment reminders |
| Conservative (24+ hours) | ✅ Minimal user disruption ✅ Lowest costs ✅ Respects preferences | ❌ Poor for urgent messages ❌ May be too slow ❌ Lower reliability | Marketing, newsletters |
The key is matching timeout periods to message urgency and user expectations. Critical security alerts need immediate fallback - users expect these messages within minutes, not hours. On the other hand, order confirmations can afford longer grace periods since users understand that detailed information might take time to process.
Consider your users' daily routines too. A push notification sent during work hours might not be seen for several hours, making email a valuable fallback. But evening notifications often get immediate attention, so longer timeout periods make sense.
Respecting User Preferences
The most sophisticated fallback strategy means nothing if it annoys your users. Courier automatically respects user communication preferences across all channels, ensuring fallback messages only go through channels users have opted into.
This creates an interesting challenge: what happens when a user has opted out of all your fallback channels except one? Smart routing becomes even more important. You might prioritize email for detailed information but still need SMS for truly critical alerts like security breaches or payment failures.
The solution is contextual fallback rules. Users might opt out of marketing SMS but still want security alerts via text. Courier's preference system lets you create these nuanced routing decisions that respect user choice while ensuring critical information gets through.
How Do You Handle Provider Failures?
Channel fallbacks protect against user-side issues, but what happens when your notification providers themselves have problems? Provider failures are more common than you might think - even major services like SendGrid, Twilio, or Firebase Cloud Messaging experience outages.
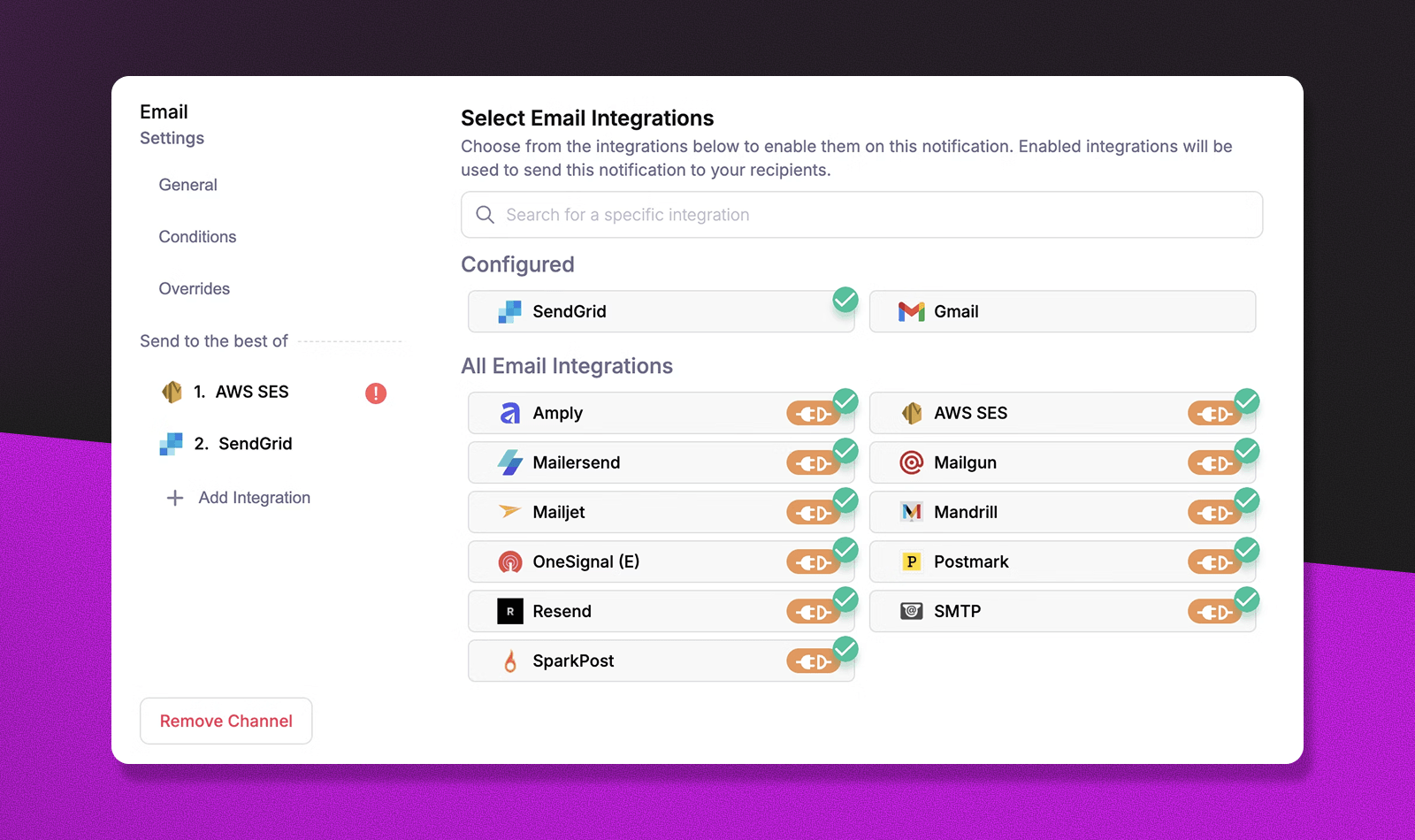
Courier's provider failover system creates redundancy within each channel. If your primary email provider is experiencing delays, the system automatically switches to your backup provider without affecting the user experience. This happens transparently - users never know there was a problem.
The key is configuring multiple providers for your most critical channels. Most teams set up backup email and SMS providers, since these channels often handle the most important fallback messages. Push notifications benefit from provider redundancy too, especially for apps that serve both iOS and Android users across different geographic regions.
What About Cost Optimization?
SMS costs can add up quickly, especially for high-volume applications. While push notifications and email are essentially free after setup, SMS can range from a few cents to over fifty cents per message depending on the destination country.
The smart approach is conditional fallback routing. Not every message needs the full fallback chain - marketing updates might only fallback from push to email, while security alerts get the complete push-to-SMS-to-email treatment. This keeps costs manageable while ensuring critical messages always get through.
Consider your message volume too. If you're sending thousands of notifications daily, even small SMS costs become significant. Many teams reserve SMS fallbacks for their most valuable user segments or highest-priority message types, using email as the primary fallback for everything else.
How Do You Monitor Fallback Performance?
Effective fallback strategies require continuous monitoring and optimization. Without proper tracking, you might not realize that your primary channels are failing more often than expected, or that your fallback timing is too aggressive.
The most important metrics to track are fallback usage rates by channel and message type. If more than 30% of your push notifications are falling back to other channels, that suggests a problem with your push setup, user engagement, or token management that needs investigation.
Delivery time analytics are equally valuable. If messages consistently take longer to deliver through fallback channels, you might need to adjust your timeout periods or reconsider your channel priority order. The goal is finding the sweet spot where critical messages get through quickly without overwhelming users with duplicate notifications.
Advanced Fallback Patterns
Geographic Routing
Channel preferences vary significantly by region. European users often prefer WhatsApp for business communications, while US users are more responsive to SMS. Asian markets might favor different messaging platforms entirely. In business environments, Slack dominates in tech companies, while Microsoft Teams is prevalent in enterprise organizations.
The key is understanding your user base and their regional communication patterns. What works in one market might be ineffective or even intrusive in another. Courier's routing system lets you adapt your fallback strategies based on user location and workplace culture, ensuring messages reach users through their preferred regional and professional channels.
Time-Based Routing
Message urgency should drive your fallback timing and channel selection. Critical security alerts need immediate multi-channel delivery, while routine updates can afford longer grace periods between fallback attempts.
Consider user behavior patterns too. Messages sent during business hours might not be seen for hours, making email a valuable fallback. Evening notifications often get immediate attention, so you can afford longer timeout periods before triggering fallbacks.
User Behavior-Based Fallbacks
The most sophisticated fallback strategies adapt based on how individual users typically engage with your notifications. Some users are email-first communicators who rarely check push notifications. Others are mobile-native and respond quickly to push but ignore email.
By tracking user engagement patterns across channels, you can personalize fallback strategies to match individual preferences. This improves delivery rates while respecting how users actually want to receive information.
Common Implementation Mistakes to Avoid
Don't Set Timeouts Too Short
One of the most common mistakes is setting overly aggressive timeout periods. Five-second timeouts might seem efficient, but they don't account for normal network delays, temporary connectivity issues, or provider processing time.
Reasonable timeout periods give your primary channels a fair chance to succeed before triggering fallbacks. Most successful implementations use 1-5 minute timeouts for providers and 5-30 minute timeouts for channels, depending on message urgency.
Don't Ignore User Preferences
Respecting user communication preferences is both a legal requirement and a user experience necessity. Forcing messages through channels users have opted out of damages trust and can violate regulations like GDPR or CAN-SPAM.
The right approach is sequential fallback routing that respects user preferences at each step. If a user has opted out of SMS, the system should skip that channel entirely and move to the next available option in your fallback chain.
What Are Real-World Fallback Use Cases?
Different industries have unique notification challenges that make fallback messaging essential. Understanding how leading companies handle these scenarios can help you design better strategies for your own applications.
Healthcare Communications
Healthcare organizations deal with life-critical communications where message delivery isn't optional. Appointment reminders need multiple touchpoints because missed appointments cost healthcare systems billions annually. When a push notification about an upcoming surgery or critical test doesn't reach a patient, the fallback to SMS and email ensures they receive this vital information.
Prescription refill notifications present another challenge. Patients might ignore a push notification, but an email with detailed pickup instructions and pharmacy contact information serves as a valuable reference. For time-sensitive medications, SMS fallbacks ensure patients get immediate alerts when refills are ready.
Test results notifications require careful handling too. Push notifications provide immediate awareness that results are available, while email fallbacks offer secure portal access and detailed next steps. This multi-channel approach respects patient preferences while ensuring critical health information reaches them reliably.
SaaS Platform Alerts
SaaS companies face unique challenges with user engagement and system reliability. When your application experiences downtime, users need to know immediately - but they might not have your app installed or push notifications enabled.
System status alerts demonstrate the value of intelligent fallbacks. A push notification provides instant awareness to active users, while Slack or Microsoft Teams alerts reach entire development and operations teams instantly. SMS ensures that administrators and key stakeholders receive critical updates even when they're away from their devices, and email serves as a detailed record of the incident and resolution steps.
Security breach notifications follow similar patterns. Push alerts reach users quickly, but Slack/Teams notifications ensure that security teams get immediate visibility into critical issues. SMS fallbacks provide an additional layer for security-critical information, especially when users haven't opened your app recently. The urgency of security communications makes multi-channel fallback strategies essential, not optional.
HR and Employee Communications
HR departments manage communications that directly impact people's livelihoods and well-being. Benefits enrollment deadlines, policy changes, and emergency notifications can't afford to be missed due to channel failures.
Open enrollment reminders illustrate this perfectly. An initial push notification creates awareness, but employees need detailed information about their options. Email fallbacks provide comprehensive benefits comparisons and enrollment links, while Slack or Teams notifications reach employees during work hours when they're most likely to take action. SMS serves as urgent deadline reminders for those who might miss other channels.
Emergency workplace notifications require even more robust fallback strategies. Weather-related closures, security incidents, or urgent policy changes need to reach every employee quickly. Push notifications alert those with company apps, Slack/Teams messages reach employees instantly during work hours, SMS ensures coverage for remote workers or those without workplace chat access, and email provides detailed instructions and documentation.
Marketplace Transactions
Marketplace platforms coordinate complex interactions between buyers, sellers, and service providers. Transaction notifications, delivery updates, and dispute resolutions require reliable delivery to maintain trust and facilitate smooth commerce.
Order status updates showcase the importance of fallback messaging. Buyers expect immediate notification when their order ships, but they also need detailed tracking information and delivery instructions. Push notifications provide instant awareness, email offers comprehensive tracking details, and SMS serves as final delivery alerts when packages are out for delivery.
Payment notifications require particular care in marketplace environments. When a payment fails or requires additional verification, both buyers and sellers need immediate notification. Push alerts provide instant awareness, while SMS fallbacks ensure critical payment issues get resolved quickly to avoid transaction delays.
Developer Platform Communications
Developer platforms serve technical audiences with specific communication needs. API limit warnings, service updates, and security advisories require precise timing and reliable delivery to maintain developer trust and platform stability.
API rate limiting notifications demonstrate the complexity of developer communications. A push notification might alert developers to approaching limits, but they need detailed information about usage patterns and optimization strategies. Slack or Teams notifications work perfectly for development teams who live in these platforms, while email provides comprehensive analytics and recommendations, and SMS serves as urgent alerts when limits are actually exceeded.
Security advisories for developer platforms require immediate and comprehensive communication. Push notifications create instant awareness of vulnerabilities or required updates, while Slack/Teams alerts reach entire development teams instantly during work hours. Email provides detailed technical information, patch instructions, and timeline expectations. The technical nature of these communications makes multi-channel fallback strategies crucial for ensuring developers receive critical security information through their preferred professional channels.
Setting Up Your First Fallback Configuration with Courier
Getting started with fallback messaging is straightforward, but the key is starting simple and evolving your strategy based on real user behavior and delivery data.
Most successful implementations begin with a basic two-channel fallback: push to email for standard notifications, or push to SMS for critical alerts. This covers the majority of delivery scenarios without overwhelming users or inflating costs.
The beauty of Courier's approach is that you can start with simple configurations and add complexity as your needs grow. Begin by identifying your most critical notification types - the messages that absolutely must reach users. These are your candidates for multi-channel fallback strategies.
For standard notifications like order confirmations or account updates, a simple push-to-email fallback often provides the right balance of reliability and user experience. Users get immediate awareness through push, but have detailed information available in their email when they need it.
What's Next?
Fallback messaging ensures your notifications reach users regardless of channel availability. With Courier's intelligent routing, you can build resilient notification systems that automatically adapt to delivery challenges.
Start building with Courier's multi-channel routing to implement intelligent fallbacks in your notification system. Configure user preferences to respect communication choices while maintaining reliability. For complex scenarios, explore workflow automations to create sophisticated routing logic.
Ready to ensure every critical message reaches your users? Request a demo to see how Courier's fallback messaging can improve your notification delivery rates, or sign up free to start building resilient notification systems today.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly should push notifications fall back to email?
The ideal fallback timing depends on message urgency. For critical alerts, wait 1-2 minutes before falling back. For standard notifications, 5-30 minutes allows for temporary connectivity issues to resolve. Always consider your specific use case and user expectations.
Can users opt out of fallback channels?
Yes, Courier respects user preferences across all channels. If a user opts out of SMS, the system will skip that channel even in fallback scenarios. However, you can configure whether to attempt delivery through opted-out channels for critical security or transactional messages where user safety is paramount.
What happens if all channels fail?
When all channels fail, Courier logs the failure and triggers webhooks for your error handling. Implement monitoring to catch these scenarios and consider alternative communication methods like in-app notifications, support ticket creation, or manual outreach for critical messages.
How do fallbacks affect delivery analytics?
Courier tracks which channel ultimately delivered each message, including fallback attempts. You can analyze fallback rates, channel performance, delivery times, and user engagement patterns through analytics APIs or webhook events to continuously optimize your routing strategy.
Should marketing messages use fallback channels?
Generally, marketing messages should respect channel preferences strictly and avoid aggressive fallback strategies. Reserve fallbacks for transactional or critical communications. Sending promotional content through fallback channels may violate user expectations, increase unsubscribe rates, and potentially breach regulations like GDPR or CAN-SPAM.
How do international deliveries affect fallback strategies?
International delivery requires region-specific strategies. SMS costs vary dramatically by country (from $0.01 to $0.50+ per message), push notification support differs by region, and email deliverability can be affected by local providers and regulations. Configure region-specific routing rules and test thoroughly in each market.
How do you detect if users have disabled push notifications?
Monitor push token validity and delivery receipts to identify users who may have disabled notifications. When push consistently fails for specific users, tag them for alternative communication strategies. You can also implement in-app prompts to re-enable notifications or collect alternative contact preferences.
What's the best grace period between fallback attempts?
Grace periods should match message urgency and user behavior patterns. Critical alerts need 2-5 minutes, transactional updates can wait 30 minutes to 2 hours, and marketing messages might allow 24-48 hours. Test different timing strategies and measure engagement rates to find your optimal windows.
How do you measure fallback effectiveness?
Track key metrics like fallback usage rates, channel-specific engagement, delivery success rates, and user satisfaction. Set up alerts when fallback rates exceed normal thresholds (typically 20-30%), indicating potential issues with your primary channels that need investigation.
Similar resources

Expo Push Notifications: The Complete Implementation Guide (SDK 52+)
Expo push notifications are alerts sent from a server to a user's phone, even when the app isn't open. To set them up, install the expo-notifications library, ask the user for permission, and get a unique push token for their device. Your server sends a message to Expo's push service with that token, and Expo delivers it through Apple or Google. Push notifications only work on real phones, not simulators. Local notifications are different — they're scheduled by the app itself for things like reminders. You can also route Expo push through services like Courier to add email, SMS, and Slack fallbacks.
By Kyle Seyler
February 24, 2026

Best Email API Providers for Developers in 2026: SendGrid vs Postmark vs Mailgun vs SES vs Resend
Your email provider sticks with you longer than most technical decisions. Courier handles notification infrastructure for thousands of teams, so we went deep on the six email providers that show up most: SendGrid, Postmark, Mailgun, Amazon SES, Resend, and SMTP. This guide covers real API primitives, actual code from each provider's docs, Courier integration examples with provider overrides, and an honest read on where each developer experience holds up and where it breaks down. We also asked Claude to review every API and tell us which one it would wire up first. The answer surprised us.
By Kyle Seyler
February 23, 2026
What's the Difference Between Omnichannel & Multichannel
Most teams say "omnichannel" when they mean "multichannel," and in most cases the distinction doesn't matter much. But if you truly want to provide an exceptional customer engagement experience you should know the difference. Both involve sending messages across email, push, SMS, Slack, and in-app. They terms diverge when those channels know about each other. Multichannel means you can reach users on multiple channels. Omnichannel means those channels share state, so a user who reads a push notification won't get the same message via email an hour later. This guide breaks down the real distinctions, when the difference actually matters, and which messaging platforms deliver true omnichannel coordination.
By Kyle Seyler
February 11, 2026
© 2026 Courier. All rights reserved.